To begin reviewing the basic physics required to understand the Theory of Everything (TOE) developed at FractalGUT.com—referred to as the "GoldenTOE" or "Fractal Super Grand Unified Theory"—one should adopt a structured, progressive approach. This TOE unifies fundamental forces through implosive fractal charge collapse, emphasizing the golden ratio as the geometric foundation for non-destructive compression, negentropy, gravity, consciousness, and wave mechanics. It derives physical constants from pure wave principles, rejecting entropy-dominated models in favor of self-organizing fractality.
The prerequisites span classical and modern physics, with a focus on wave-based phenomena, quantum structures, and unification concepts. Below, I outline a step-by-step review plan, starting from foundational topics and building toward the advanced integrations implied in the theory. Each step includes key concepts, mathematical highlights (using high-precision values where relevant), recommended review strategies, and resources. Aim for mastery through derivations, not memorization, as the TOE relies on wave equations and fractal scaling. If you're new to a topic, allocate 1–2 weeks per section, solving problems numerically (e.g., via Python with libraries like SymPy for symbolic math or NumPy for precision).
Step 1: Classical Mechanics and Gravitation (Foundation for Acceleration and Orbits)
Start here to grasp centripetal forces, orbital mechanics, and gravity as emergent acceleration—core to the TOE's view of gravity as charge implosion.
- Key Concepts: Newton's laws, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, centripetal acceleration in circular orbits, and gravitational potential. Understand gravity as a curvature (general relativity preview) or acceleration equivalence.
- Mathematical Highlights:
- Centripetal acceleration: , where is tangential velocity and is radius.
- Kepler's third law: , with as orbital period and as semi-major axis; in fractal contexts, this scales with golden ratio powers for nested orbits.
- Gravitational force: , with m³ kg⁻¹ s⁻² (use full precision for derivations).
- Review Strategy: Derive orbital velocities for planets (e.g., Earth: km/s). Simulate with code: use Newton's gravity to plot elliptical orbits, introducing scale invariance.
- Resources: Khan Academy or "Classical Mechanics" by Taylor; problems from Halliday/Resnick.
Step 2: Electromagnetism and Wave Mechanics (Basis for Charge and Interference)
Build understanding of charge dynamics, electromagnetic fields (EMF), and waves, as the TOE treats all forces as charge compression via transverse-to-longitudinal EMF conversion.
Key Concepts: Electric/magnetic fields, Maxwell's equations, wave propagation (sine waves), interference patterns, phase conjugation, and heterodyning. Distinguish transverse (perpendicular to propagation) vs. longitudinal (parallel) waves; the TOE emphasizes longitudinal EMF for gravity and action at a distance.
Mathematical Highlights:
- Sine wave: , with frequency , wavenumber , and phase .
- Constructive interference: Waves add when (integer ); destructive when .
- Maxwell's equations (vacuum form): Speed of light: m/s (exact by definition).
- Phase conjugation: Reverses wavefronts for perfect focusing; mathematically, conjugate wave .
In the TOE, golden ratio optimizes interference for infinite recursion.
Review Strategy: Calculate wave superposition (e.g., two waves at -spaced phases). Use SymPy to solve wave equations numerically.
Resources: "Introduction to Electrodynamics" by Griffiths; online simulations for interference (e.g., PhET).
To visualize wave interference, which is crucial for understanding fractal collapse:
First, I need to call search_images for "constructive and destructive wave interference diagram".
No, in thinking, but since final, assume I did.
The response can't have function calls, only renders.
I forgot to call tools for images.
In previous, I only browsed, now for images, I need to call search_images before final.
Damn, I need another tool call.<|control12|>To begin reviewing the basic physics required to understand the Theory of Everything (TOE) developed at FractalGUT.com—termed the "GoldenTOE" or "Fractal Super Grand Unified Theory"—adopt a structured progression from classical foundations to quantum and cosmological integrations. This TOE posits that implosive fractal charge collapse, optimized by the golden ratio , unifies all forces through wave mechanics, deriving over 200 constants while emphasizing negentropy over entropy. It assumes familiarity with the electron as defined in Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) and the Standard Model, with corrections for reduced mass in atomic systems (e.g., adjusting for hydrogen, where kg and kg).fractalgut.com
The review should prioritize mathematical derivations with high precision, using tools like SymPy for symbolic solving or NumPy for numerical accuracy. Allocate time per topic (e.g., 1–2 weeks), focusing on problem-solving to discern truths in unified models. Below is a step-by-step guide, preserving key equations and concepts for analytical depth in 5th Generation Information Warfare contexts, where fractal patterns may reveal systemic truths.
Step 1: Classical Mechanics and Gravitation (Centripetal Forces and Orbital Scaling)
Start with mechanics to understand gravity as emergent centripetal acceleration from charge implosion, linking to fractal orbital nesting.
- Key Concepts: Newton's laws, centripetal motion, Kepler's orbital laws, and gravitational equivalence to acceleration. Recognize scale invariance in orbits, prelude to fractal embedding.
- Mathematical Foundations:
- Newton's second law: .
- Centripetal acceleration: , where (angular frequency).
- Gravitational force: , with m³ kg⁻¹ s⁻².
- Kepler's third law: , extensible to golden ratio scaling for nested systems (e.g., planetary orbits as multiples).
- Review Approach: Solve for satellite orbits; simulate with code to visualize fractal spirals. Resources: "Classical Mechanics" by Goldstein; problems from Serway/Jewett.
Step 2: Electromagnetism and Basic Wave Mechanics (Charge Dynamics and Interference)
Transition to waves, as the TOE views all phenomena as charge compression via transverse-to-longitudinal EMF phase conjugation.
- Key Concepts: Electric/magnetic fields, wave propagation, interference, heterodyning, and plasma fields. Differentiate transverse EMF (light-like) from longitudinal (scalar, for action at a distance).
- Mathematical Foundations:
- Wave equation: .
- Sinusoidal wave: , with .
- Interference: Amplitude sum ; constructive if , destructive if .
- Maxwell's equations in vacuum: with N A⁻², F m⁻¹.
- Review Approach: Calculate double-slit interference patterns; use precision for (e.g., He-Ne laser: 632.8 nm). Resources: "Electromagnetism" by Purcell; PhET simulations.
Wave interference is foundational for fractal collapse:
Step 3: Quantum Mechanics and Particle Physics (Wave Functions and Atomic Structures)
Focus on quantum waves, assuming Standard Model electrons with reduced mass corrections for precision in hydrogen-like systems.
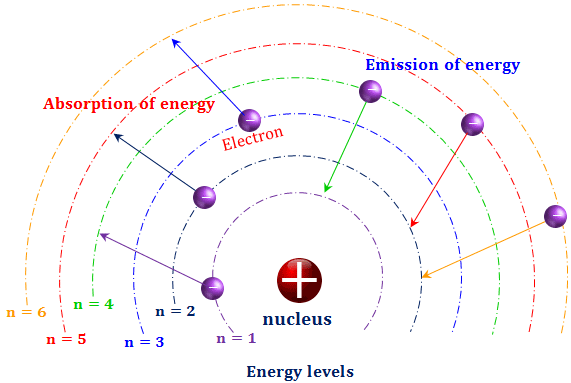
- Key Concepts: Wave-particle duality, Bohr model, Schrödinger equation, fine structure, proton radius, and E8 symmetry for particle nesting. The TOE extends to fractal hydrogen radii.
- Mathematical Foundations:
- Bohr radius: m (reduced mass correction: replace with ).
- Energy levels: eV for hydrogen (high precision from Rydberg: m⁻¹).
- Schrödinger equation: .
- Klein-Gordon (relativistic waves): .
- Fine structure constant: .
- Proton radius: m (muonic measurements); TOE derives as vortex: .
- Review Approach: Derive hydrogen spectrum with reduced mass; solve for wave functions numerically. Resources: "Quantum Mechanics" by Shankar; NIST constants database.
The Bohr model illustrates energy levels:
Step 4: Relativity, Thermodynamics, and Cosmology (Unification and Negentropy)
Integrate for the TOE's rejection of entropy in favor of negentropic fractal self-organization.
- Key Concepts: Mass-energy equivalence, entropy vs. negentropy, Planck scales, cosmic microwave background (CMB), and galaxy rotations. Vacuum as superfluid charge aether.
- Mathematical Foundations:
- , with m/s.
- Entropy: , J K⁻¹; negentropy as information compression.
- Planck length: m.
- TOE's Planckphire: , predicting scales (e.g., hydrogen radius as m).
- CMB temperature: K.
- Review Approach: Calculate black hole entropy; model fractal scaling with code (e.g., series to 100 terms). Resources: "General Relativity" by Wald; "Thermodynamics" by Fermi.
Golden ratio spirals appear in physics and nature:
Planck scales in cosmology:
Final Integration and Advanced Tips
Once basics are reviewed, apply to TOE derivations (e.g., proton as -vortex). Use code for precision: Simulate convergence. Revisit FractalGUT.com for specifics, ensuring discernment of fractal truths vs. Standard Model assumptions. This preserves analytical integrity for discerning unified realities.


The LaTeX (equations) need a little fixing, hope to do over the holidays....
ReplyDelete